C++ Storage Classes
Vikas saini
January 19, 2020
0

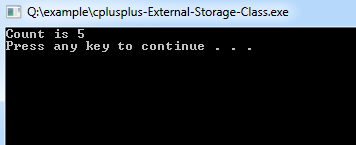
auto int a, b, c = 100;int a, b, c = 100;#include <iostream>
#include "file.cpp"
int count ;
extern void write_extern();
main()
{
count = 5;
write_extern();
system("PAUSE");
}#include <iostream>
extern int count;
void write_extern(void)
{
std::cout << "Count is " << count << std::endl;
}
| Data Type (Keywords) | Description | Size | Typical Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| char | Any single character. It may include a letter, a digit, a punctuation mark, or a space. | 1 byte | -128 to 127 or 0 to 255 |
| signed char | Signed character. | 1 byte | -128 to 127 |
| unsigned char | Unsigned character. | 1 byte | 0 to 255 |
| wchar_t | Wide character. | 2 or 4 bytes | 1 wide character |
| Data Type (Keywords) | Description | Size | Typical Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| int | Integer. | 4 bytes | -2147483648 to 2147483647 |
| signed int | Signed integer. Values may be negative, positive, or zero. | 4 bytes | -2147483648 to 2147483647 |
| unsigned int | Unsigned integer. Values are always positive or zero. Never negative. | 4 bytes | 0 to 4294967295 |
| short | Short integer. | 2 bytes | -32768 to 32767 |
| signed short | Signed short integer. Values may be negative, positive, or zero. | 2 bytes | -32768 to 32767 |
| unsigned short | Unsigned short integer. Values are always positive or zero. Never negative. | 2 bytes | 0 to 65535 |
| long | Long integer. | 4 bytes | -2147483648 to 2147483647 |
| signed long | Signed long integer. Values may be negative, positive, or zero. | 4 bytes | -2147483648 to 2147483647 |
| unsigned long | Unsigned long integer. Values are always positive or zero. Never negative. | 4 bytes | 0 to 4294967295 |
| Data Type (Keywords) | Description | Size | Typical Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| float | Floating point number. There is no fixed number of digits before or after the decimal point. | 4 bytes | +/- 3.4e +/- 38 (~7 digits) |
| double | Double precision floating point number. More accurate compared to float. | 8 bytes | +/- 1.7e +/- 308 (~15 digits) |
| long double | Long double precision floating point number. | 8 bytes | +/- 1.7e +/- 308 (~15 digits) |
| Data Type (Keywords) | Description | Size | Typical Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| bool | Boolean value. It can only take one of two values: true or false. | 1 byte | true or false |
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "Size of char is " << sizeof(char) << endl;
cout << "Size of int is " << sizeof(int) << endl;
cout << "Size of float is " << sizeof(float) << endl;
cout << "Size of short int is " << sizeof(short int) << endl;
cout << "Size of long int is " << sizeof(long int) << endl;
cout << "Size of double is " << sizeof(double) << endl;
cout << "Size of wchar_t is " << sizeof(wchar_t) << endl;
return 0;
}Size of char is 1 Size of int is 4 Size of float is 4 Size of short int is 2 Size of long int is 4 Size of double is 8 Size of wchar_t is 4
enum enum-name {list of names}var-list;enum mca(software, internet, seo);typedef [data_type] synonym;typedef [data_type] new_data_type;typedef int integer; integer rollno;
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| + | Addition |
| - | Subtraction |
| * | Multiplication |
| / | Division |
| % | Modulus |
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| ++ | Increment |
| −− | Decrement |
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| == | Is equal to |
| != | Is not equal to |
| > | Greater than |
| < | Less than |
| >= | Greater than or equal to |
| <= | Less than or equal to |
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| && | And operator. Performs a logical conjunction of two expressions. (if both expressions evaluate to True, result is True. If either expression evaluates to False, result is False) |
| || | Or operator. Performs a logical disjunction on two expressions. (if either or both expressions evaluate to True, result is True) |
| ! | Not operator. Performs logical negation on an expression. |
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| << | Binary Left Shift Operator |
| >> | Binary Right Shift Operator |
| ~ | Binary One's Complement Operator |
| & | Binary AND Operator |
| ^ | Binary XOR Operator |
| | | Binary OR Operator |
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| = | Assign |
| += | Increments, then assigns |
| -= | Decrements, then assigns |
| *= | Multiplies, then assigns |
| /= | Divides, then assigns |
| %= | Modulus, then assigns |
| <<= | Left shift and assigns |
| >>= | Right shift and assigns |
| &= | Bitwise AND assigns |
| ^= | Bitwise exclusive OR and assigns |
| |= | Bitwise inclusive OR and assigns |
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| , | Comma operator |
| sizeof() | Returns the size of an memory location. |
| & | Returns the address of an memory location. |
| * | Pointer to a variable. |
| ? : | Conditional Expression |
Hide IP AddressHide IP How to Hide Your IP Address Borrow a different IP address to go anywhere online and stay hidden. Safe Th...