Sunday, January 19, 2020
C++ Storage Classes
About Vikas saini
Way2themes is a blogger resources site is a provider of high quality blogger template with premium looking layout and robust design
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)

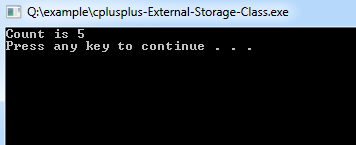
auto int a, b, c = 100;int a, b, c = 100;#include <iostream>
#include "file.cpp"
int count ;
extern void write_extern();
main()
{
count = 5;
write_extern();
system("PAUSE");
}#include <iostream>
extern int count;
void write_extern(void)
{
std::cout << "Count is " << count << std::endl;
}
About Vikas saini
Way2themes is a blogger resources site is a provider of high quality blogger template with premium looking layout and robust design
Hide IP AddressHide IP How to Hide Your IP Address Borrow a different IP address to go anywhere online and stay hidden. Safe Th...
No comments:
Post a Comment