Constants are like a variable, except that their value never changes during the program execution once defined.
What are Constants?
Constants refer to as fixed values, unlike variables whose value can be altered, constants - as the name implies does not change, they remain constant. Constant must have to be initialized at the time of creating it, and new values cannot be assigned later to it.
Constant Definition in C++
There are two other different ways to define constants in C++. These are:
Constants are like a variable, except that their value never changes during the program execution once defined.
What are Constants?
Constants refer to as fixed values, unlike variables whose value can be altered, constants - as the name implies does not change, they remain constant. Constant must have to be initialized at the time of creating it, and new values cannot be assigned later to it.
Constant Definition in C++
There are two other different ways to define constants in C++. These are:
Constant Definition by Using const Keyword
Syntax:
const type constant_name;
Example:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
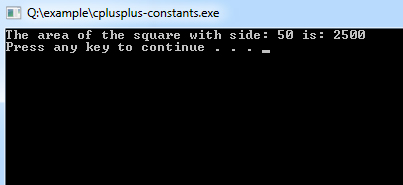
const int SIDE = 50;
int area;
area = SIDE*SIDE;
cout<<"The area of the square with side: " << SIDE <<" is: " << area << endl;
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
}
Program Output:

It is also possible to put const either before or after the type.
int const SIDE = 50;
or
const int SIDE = 50;Constant Definition by Using #define preprocessor
Syntax:
#define constant_name;
Example:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define VAL1 20
#define VAL2 6
#define Newline '\n'
int main()
{
int tot;
tot = VAL1 * VAL2;
cout << tot;
cout << Newline;
}





No comments:
Post a Comment